A new drug might help prevent a global crisis
Some experts have called antimicrobial resistance the next worldwide health crisis. A new class of antibiotics has provided science with the hope of tackling it.
According to a study in Nature, the new substance, Zosurabalpin, was effective against highly resistant bacteria in mouse pneumonia and sepsis cases.
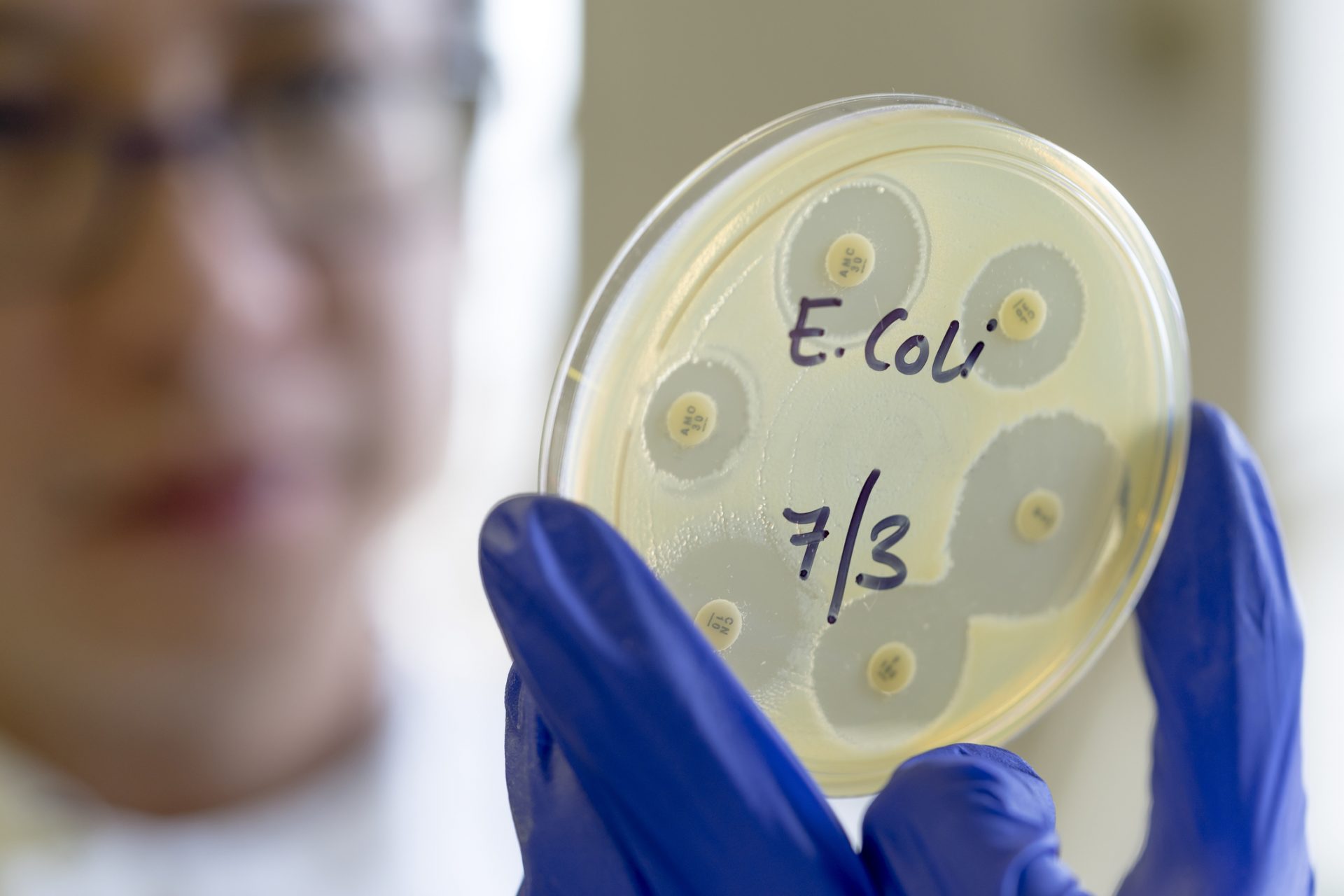
The Guardian reported that the bacteria Zosurabalpin killed was one of the top three bacteria considered to pose the greatest risk for humanity.
The World Health Organization (WHO) classified Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (Crab) as a top-priority critical pathogen alongside two other resistant bacteria.
Dr Andrew Edwards, a senior lecturer in molecular microbiology at Imperial College London, told The Guardian that Crab is a cause of infection in hospitals, primarily through ventilators.
Hospitals are a breeding ground for many resistant germs. According to the CDC, staying in a healthcare facility puts you at risk of getting an antibiotic-resistant infection.
In healthcare settings, the most risky bacteria are the ones in the gram-negative group. They can cause pneumonia, bloodstream infections, wound or surgical site infections, and meningitis.
The CDC claims gram-negative bacteria are increasingly resistant to most available antibiotics. An outer layer protects them, and they can quickly adapt to fight antibiotics.
Worldwide, according to the WHO, 1.2 million people have died from a confirmed drug-resistant infection in 2019. These germs were also partially responsible for 5 million deaths.
Both the WHO and the CDC have warned that antimicrobial resistance is an urgent global public health threat. It also puts many medical procedures at risk.
Antimicrobial resistance profoundly affects the ability of medical personnel to treat infections and extends the risks of side effects and other illnesses on patients.
It can also damage other medical treatments that depend on our capacity to avoid infections, like surgery, transplants, cancer therapy, and the treatment of chronic diseases.
Zosurabalpin's development is promising because it provides a new approach to finding drugs. It affects germs differently than previous antibiotics.
According to The Guardian, the new drug focuses on the LPS barrier that allows gram-negative bacteria to live in any environment and easily resist antibiotics.
Specifically, Zosurabalpin prevents the transportation of the substance to the outer layer of the bacterium, killing it and reducing the infection.
The newspaper cited experts who spoke about other drugs in development that also tackle the LPS barrier, so this can begin a new phase in the battle against antimicrobial resistance.
More for you
Top Stories