From ‘Shrinkflation’ to ‘Stretchflation’: how companies hide rising costs
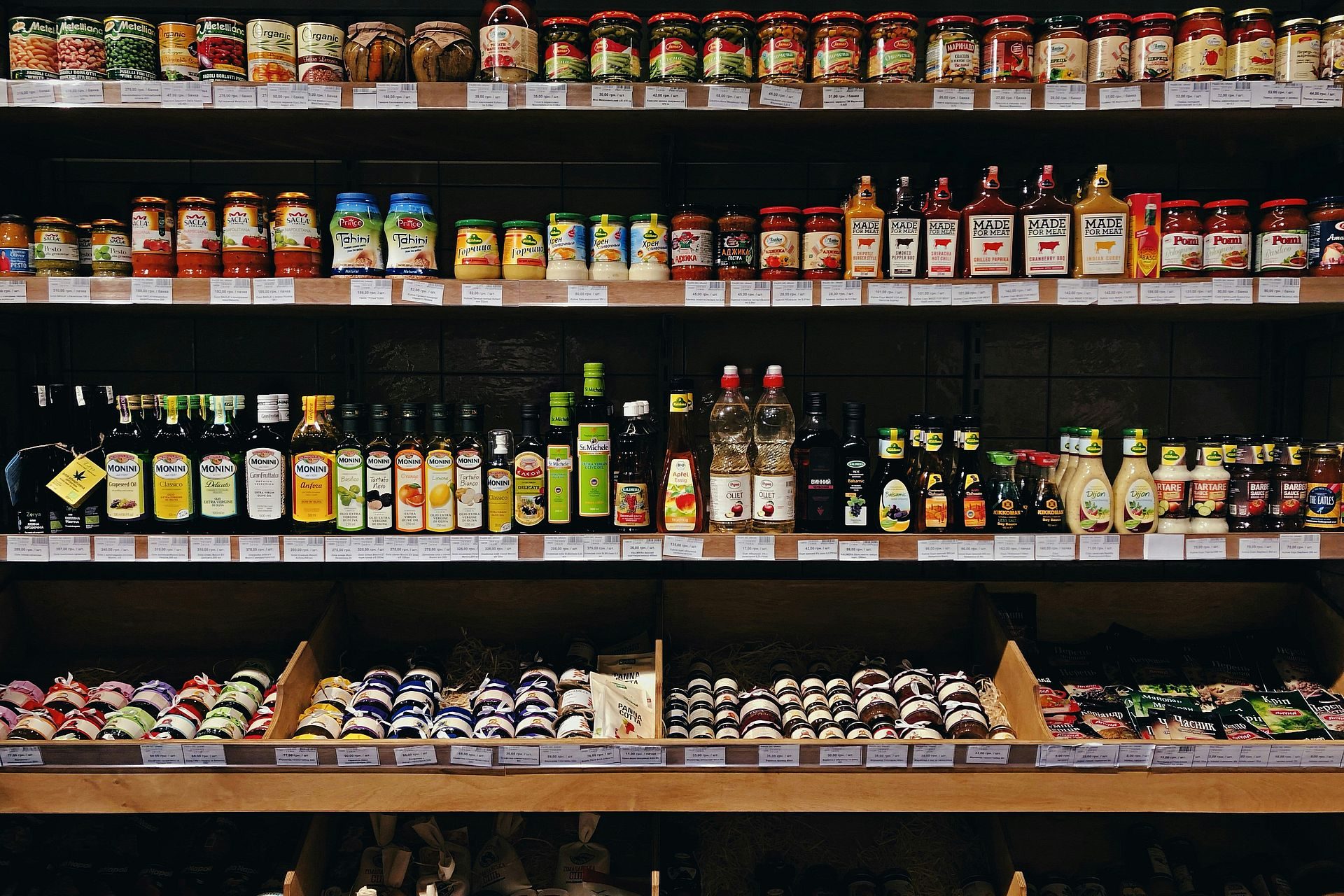
You’re probably familiar with ‘shrinkflation’: the practice of reducing a product’s amount of volume while selling it at the same price. But because it is now regulated, companies are getting more creative in hiding rising costs.
Another example is ‘cheapflation’, the practice of using lower-end and less expensive ingredients in products sold at the same or even higher prices than before.
The most recent and not-so-known strategy to disguise price increase is known as “stretchflation.” From the verb “to stretch”, this term designates an ingenious new tactic. Let’s learn more about it.
This strategy involves slightly increasing the product’s volume, as well as increasing the price; only more than it’s proportionally adequate, in order to hide inflation.
French journalist Olivier Dauvers, who specializes in mass distribution, illustrated this phenomenon with a case spotted in a supermarket: frozen bread sold for 2.93 euros ($3.28) for 400 grams can now also be found at 3.99 euros ($4.34) for 460 grams.
So in Dauvers’ example, the quantity increased by 15%, but the total price by about 35%. Rising from 7.33 ($7.97) to 8.67 euros ($9.42), the price per kilo is indicative of the increase: it is this indicator that consumers must monitor to avoid being cheated in a context of persistent inflation.
But this is not always possible for the consumer. In France, the Directorate General for Competition, Consumption and Fraud Repression, says the per-kilo price display doesn’t apply to certain pre-packaged products “for technical reasons.”
Said French administration cites for example "bags of aromatic plants weighing less than 30 g, certain sugars, jams weighing less than 50 g, certain cheeses sold by the piece", for which display per kilo is not mandatory.
Photo: Daria Volkova / Unsplash
Other products that benefit from this exemption, are certain liquids, water, ice creams and sorbets, but also bread and pastries.
‘Stretchflation’ is the latest example of the ingenious ways in which distributors disguise price increases for consumers while inflation has not yet disappeared. But will this practice soon be regulated by public authorities?
More for you
Top Stories